Bypass Surgery
What is Heart Bypass Surgery?
Heart bypass surgery, or coronary artery bypass surgery, is used to replace damaged arteries that supply blood to your heart muscle. A surgeon uses blood vessels taken from another area of your body to repair the damaged arteries. Doctors performed 213,700 such surgeries in the United States in 2011.
This surgery is done when coronary arteries become blocked or damaged. These arteries supply your heart with oxygenated blood. If these arteries are blocked or blood flow is restricted, the heart doesn’t work properly. This can lead to heart failure.
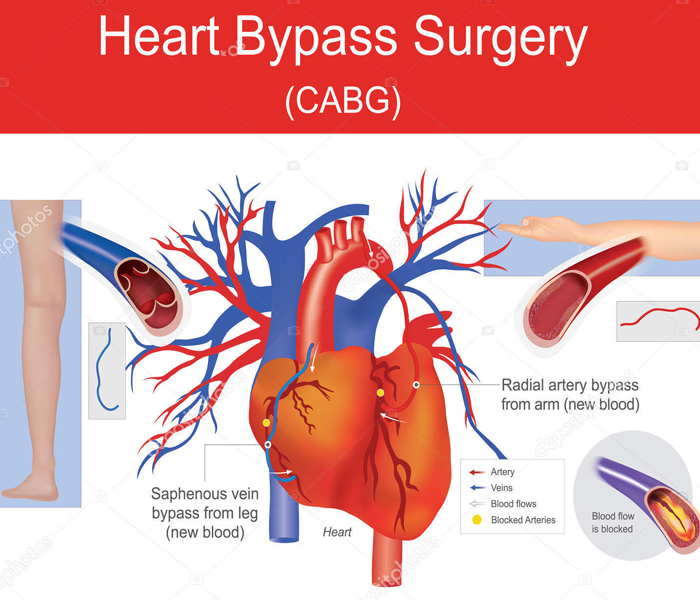
What are the different types of heart bypass surgery?
Your doctor will recommend a certain type of bypass surgery depending on how many of your arteries are blocked.
Your risk of having a heart attack, heart failure, or another cardiac issue depends on the number of arteries blocked. Blockage in more arteries also means that the surgery may take longer or become more complex.
Why might a person need heart bypass surgery?
When a material in your blood called plaque builds up on your arterial walls, less blood flows to the heart muscle. The muscle is more likely to become exhausted and fail if it’s not receiving enough blood.
Any damage this creates most often affects the left ventricle, the heart’s primary pump.
Your doctor may recommend heart bypass surgery if your coronary arteries become so narrowed or blocked that you run a high risk of a heart attack.
This condition is called coronary artery disease, or atherosclerosis. Your doctor will recommend bypass surgery when the blockage is too severe to manage with medication or other treatments.